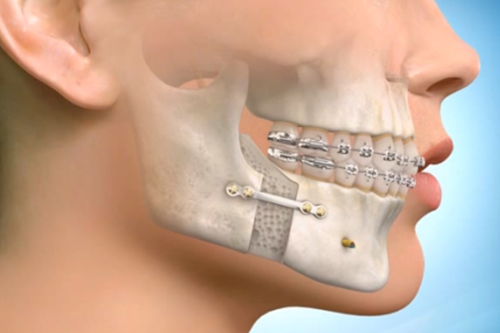
Jaw surgery, medically known as orthognathic surgery, is a specialized procedure designed to correct irregularities of the jaw bones and realign the jaws and teeth to improve function and appearance هزینه جراحی فک. It’s often recommended when conventional orthodontic treatments like braces alone cannot resolve severe bite problems or jaw misalignments.
What is Jaw Surgery?
Jaw surgery involves the surgical repositioning of the upper jaw (maxilla), lower jaw (mandible), or both. The goal is to correct skeletal deformities that affect chewing, speaking, breathing, or facial aesthetics. This surgery can be performed on adolescents or adults once facial growth is complete.
Common Conditions Requiring Jaw Surgery
Several conditions may necessitate jaw surgery, including:
-
Malocclusion (Bad Bite): When the upper and lower teeth don’t align properly, causing overbite, underbite, crossbite, or open bite.
-
Jaw Misalignment: When the jaws are too far forward or backward, or uneven in size.
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders: Severe TMJ problems causing pain or dysfunction.
-
Sleep Apnea: Structural jaw problems contributing to obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Facial Trauma: Correcting jaw fractures or deformities after an injury.
-
Congenital Conditions: Birth defects affecting jaw development, like cleft palate.
The Jaw Surgery Process
-
Consultation and Planning: The journey starts with a consultation involving an oral and maxillofacial surgeon and often an orthodontist. They’ll perform clinical examinations, X-rays, and 3D imaging to map the jaw structure and create a detailed surgical plan.
-
Orthodontic Preparation: Many patients undergo orthodontic treatment before surgery to align the teeth properly. This phase can take 12-18 months.
-
Surgery: Under general anesthesia, the surgeon repositions the jaws by making precise cuts in the bone and securing them with plates, screws, or wires. Surgery typically lasts 1 to 4 hours, depending on complexity.
-
Recovery: Initial healing takes about 6 weeks, but full recovery and stabilization may take several months. During recovery, patients follow a soft or liquid diet and may require pain management and physical therapy.
-
Post-Surgery Orthodontics: Braces are often used post-surgery for final alignment and bite adjustments.
Benefits of Jaw Surgery
-
Improved bite and chewing function.
-
Enhanced speech clarity.
-
Relief from chronic jaw or TMJ pain.
-
Improved breathing, especially for sleep apnea sufferers.
-
Enhanced facial symmetry and appearance, boosting self-confidence.
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgery, jaw surgery carries risks such as infection, nerve injury (causing numbness), bleeding, or relapse of jaw position. Careful planning, skilled surgeons, and proper postoperative care minimize these risks.
Is Jaw Surgery Right for You?
Jaw surgery is usually recommended when non-surgical treatments can’t correct functional or aesthetic issues. If you experience chronic jaw pain, difficulty chewing, speech problems, or dissatisfaction with your facial profile, consulting an oral surgeon can help determine if surgery is a viable option.